Chapter 4: End-of-chapter exercises
Multiple Choice:
What happens when a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price in some market
A) A surplus occurs
B) A shortage occurs
C) Quantity demanded falls
D) Quantity supplied risesA city implements a rent control policy that sets maximum rental prices above the equilibrium level. What is the likely outcome?
a) Shortage of rental units
b) Surplus of rental units
c) No change in market conditions
d) More landlords willing to rent apartments
A new law sets the minimum wage above the market equilibrium. What is the expected result?
a) Increase in demand for labor
b) Decrease in demand for goods
c) Shortage of labor
d) Surplus of labor
e) No effect
Short Answer:
Consider a market with demand represented by Q = 50 - 2P and supply represented by Q = 2P + 30.
Find the equilibrium price and quantity.
Suppose a price ceiling of $18 is implemented in this market. Find the quantity demanded, quantity supplied, and quantity actually traded. Then clarify if there is a shortage or surplus.
Sketch of Solutions:
Multiple Choice:
B: A price ceiling doesn’t allow the market price to go any higher than where the ceiling is set. If the ceiling is below the equilibrium it’s a binding price control, preventing the market from reaching equilibrium. As a consequence we get a shortage (there’s a higher quantity demanded than quantity supplied, consistent with the definition of a shortage).
C: No change in market conditions because the rent control about the equilibrium price is non-binding!
D: This is a binding price control. At the above equilibrium price the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded, by definition a surplus!
Short Answer:
Consider a market with demand represented by Q = 50 - 2P and supply represented by Q = 2P +30.
Find the equilibrium price and quantity.
To find the equilibrium: Q_d = Q_s so we write:
50 - 2P = 2P + 30
20 = 4P
P* = 20
Q* = 50 - 2(20) = 10
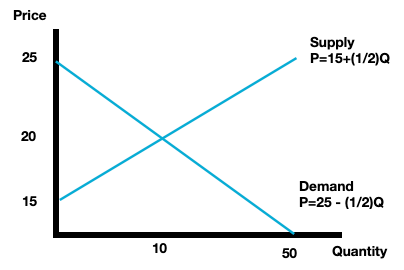
Equilibrium price is $20, equilibrium quantity is 10. Graphically:
b. Suppose a price ceiling of $18 is implemented in this market. Find the quantity demanded, quantity supplied, and quantity actually traded. Then clarify if there is a shortage or surplus.
At the price of $18, which is below the equilibrium P*=20, we will have a shortage:
First find the quantity demanded:
Q(18) = 50 - 2(18)
Q(18) = 50 - 36 = 24
Qd = 24
Then find the quantity supplied:
Q(18) = 2(18) - 30
Q(18) = 36 - 30 = 6
Qs = 6
Since Qd = 24 and Qs = 6, we have a shortage of 18 units (24 - 6 = 18).
Graphically we have the following: